Cybersecurity has become an increasingly complex and challenging field with the rise of new and sophisticated threats. To combat these threats effectively, security professionals need to have access to powerful tools that can analyze, identify, and mitigate potential risks. One such tool is Generative Artificial Intelligence, which has recently emerged as a promising solution to enhance cybersecurity defenses.
Generative AI has been making waves in various industries, from designing fashion to composing music. But how can it be utilized effectively in the field of cybersecurity? With the increasing number of cyberattacks and sophisticated techniques used by hackers, it’s crucial to have advanced tools and technologies to defend against them.
But what is it? And how can it effectively be used in cybersecurity?
What is Generative AI?
Generative AI is a subset of artificial intelligence (AI) that uses machine learning algorithms to generate new data. The system utilizes two neural networks, a generator, and a discriminator, to generate synthetic data that closely resembles the real data it was given. The discriminator evaluates the synthetic data based on its similarity to the real data. Through repeated iterations, the generator learns to produce synthetic data that closely resembles real data, which can be utilized for a multitude of purposes ranging from cybersecurity to commercial applications.
The advantage of generative AI lies in its ability to learn from itself, thus creating more accurate results with each iteration. This form of AI can generate an infinite amount of potential outcomes within its training set, without being constrained by pre-existing data such as traditional classifiers or predictors.
Generative AI has mostly been used in creative fields due to its ability to recognize patterns in data and create unique products based on those patterns. The ability to break away from traditional approaches and explore new possibilities has revolutionized creative processes by offering fresh perspectives and expanding the boundaries of what is possible. It opens doors to creative experimentation and enables artists, designers, and musicians to tap into a vast range of possibilities that were previously untapped.
Generative AI has the potential to revolutionize the way we approach cybersecurity by using machine learning algorithms to detect patterns and anomalies in data that human security analysts may miss.
But it’s not all good. It’s important to note that threat actors can also exploit Generative AI for malicious purposes, including generating sophisticated phishing or deep fake attacks. Therefore, while utilizing Generative AI in cybersecurity, organizations must implement appropriate defense mechanisms to prevent misuse and protect against emerging threats.

Why Utilize Generative AI in Cybersecurity?
Like XDR, every cybersecurity company has begun including Generative AI as part of their solutions. So, how do you make sense of the noise? It’s important to realize not all solutions are created equal. Just slapping on AI or saying you have Generative AI does make your solution that much more powerful. The fact is most solutions currently in the marketplace utilize Generative AI for search or to integrate ChatGPT-like functionality.
Generative AI, when used correctly, can effectively be used in cybersecurity in several ways by leveraging its ability to create realistic and synthetic data. Examples include:
Data Augmentation: Generative AI is capable of producing synthetic data that closely reflect real-world cybersecurity datasets to help overcome insufficient and unbalanced data. This synthetic data can then be used to supplement existing datasets to improve machine learning model training by increasing the depth and accuracy of the models’ threat detection capabilities.
Threat Actor Profiles: Generative AI can learn to anticipate the behavior of possible attackers by analyzing historical security event data. Security teams can then use this information to develop more effective security controls and better defend against future attacks.
Pen Testing and Red Teaming: Generative AI can be utilized in security testing and red teaming exercises by creating realistic attack simulations that mimic the techniques and tactics of real-world attackers. By generating simulated attacks or scenarios, security professionals can assess the effectiveness of their defenses, identify vulnerabilities, and enhance their security posture.
Malware generation: Generative AI can be trained to create fake malware samples that resemble actual threats. This can help in understanding various malware subtypes, testing the efficacy of detection and response tools, and developing preventive measures by researchers and analysts.
Threat Intelligence Integration: Generative AI can be integrated with threat intelligence feeds and databases to stay current on the latest threats, attack signatures, and indicators of compromise. By combining this external information with its internal data processing, Generative AI can identify suspicious actions with well-known threat patterns to increase the accuracy of threat detection and mitigation.

What are Some limitations of Current Cybersecurity Implementations of Generative AI?
Many solutions in the market today are reliant on First and Second Wave AI which utilize rules-based systems that are unable to scale and are only capable of detecting attacks with known signatures.
Training Data Bias: The effectiveness of generative AI models is heavily influenced by the quality and variety of the training data. If the training data is biased or incomplete, the generated outputs may also demonstrate those biases or be unable to recognize certain threat patterns. It is essential to ensure that the training data is representative and complete to prevent distorted or inaccurate results.
Labor Intensive: Training and running generative AI models can be challenging due to the significant computational resources required. Organizations with limited resources or infrastructure may face difficulties in effectively training and deploying these models.
Unpredictability: Generative AI models have the potential to produce outputs that are unpredictable or unexpected. In creative domains, this can be beneficial, but in cybersecurity, it can result in false positives or false negatives. Thorough validation and verification of the generated results is necessary to ensure their dependability and precision.
Limited Comprehension: Generative AI models may face challenges in comprehending the contextual subtleties of cybersecurity threats. They tend to concentrate on patterns and statistical analysis, which may not be adequate to comprehend intricate attack strategies or quickly changing tactics used by sophisticated adversaries.
Interpretability and Explainability: Generative AI models can be highly complex and difficult to interpret or explain. Understanding how and why a model made a specific decision or generated a certain output can be challenging, limiting the ability of cybersecurity professionals to gain insights into the underlying reasoning and potentially undermining trust in the system.
Adversarial Attacks: Generative AI models are vulnerable to adversarial attacks, where malicious actors intentionally manipulate or exploit the model’s vulnerabilities. Adversarial examples can be crafted to deceive the model and bypass its threat detection mechanisms, making it challenging to rely solely on generative AI for cybersecurity defense.
How is MixMode’s AI Different?
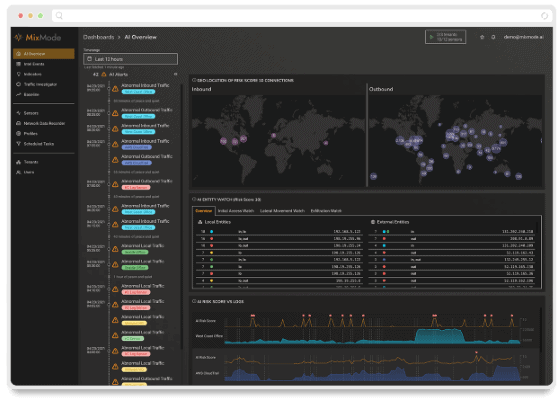
MixMode is the world’s first commercially available dynamical threat detection platform built on Third Wave AI (as defined by DARPA). It easily integrates with any security environment to understand, adapt and evolve to detect threats in real-time on its own without the need for rules, training, or tuning from humans.
By learning your environments’ normal behavior, MixMode can identify and surface known or unknown attacks in real-time, providing unparalleled threat detection capabilities and increasing the efficiency and productivity of the SOC.
Click here for a deep dive into MixMode’s AI to learn how we’re different.

MixMode: The Only Dynamical AI for Threat Detection and Response
MixMode’s patented self-learning AI platform was born out of dynamical systems and identifies patterns and trends without predefined rules or training. MixMode’s AI customizes to the specific dynamics of individual networks, rather than relying on more generic ML models typically found in First and Second wave solutions.
The MixMode Platform delivers:
Behavioral Analysis: MixMode’s AI utilizes a dynamical computational model to create a baseline of activities and determine what is normal inside a specific network. The platform is constantly evolving on its own and reacting to new deviations from this set baseline, continuously monitoring user behavior to identify variations from the initial baseline of typical behavior and surface potential threats.
Real-time Threat Detection: The MixMode Platform continuously monitors network activity, system logs, and security events in real-time, to quickly identify known and unknown threats. The Platform detects and prevents threats that bypass traditional security tools, including Zero-Day, Insider Threats, New Ransomware, “Living off the Land”, Supply Chain, and AI/ML Model Poisoning.
Predictive Analytics: The MixMode Platform utilizes historical data and dynamical algorithms to examine patterns and trends to anticipate attacks. This comprehensive approach enables the identification of potential threats, even in the absence of explicit indicators or attack signals, to enable security teams to stay one step ahead of cyber threats.
Adaptive Defense: MixMode’s AI continuously learns from the threat landscape and tailors itself for each environment to successfully identify and address new cyber threats, By continuously studying the threat landscape and adapting new methodologies, The MixMode Platform is constantly evolving to ensure that organizations have an effective defense against today’s sophisticated attacks.
Is Generative AI the same as Third Wave AI?
No, and don’t believe those cybersecurity companies jumping on the bandwagon.
DARPA defines the first wave of AI as enabling “reasoning over narrowly defined problems,” but with a poor level of certainty. The second wave, it claims, enables “creating statistical models and training them on big data,” albeit with minimal reasoning. “The Third Wave” enables machines to adapt to changing situations.
Generative AI focuses on creating new data or content rather than just analyzing or categorizing already-existing data. It involves models that are capable of producing fresh, original results based on trends and details discovered from training data. This is why generative AI has successfully been used in a variety of creative fields, including music creation, text generation, and image generation.
Third Wave AI is a broader concept that describes the advancement of AI methods and technologies. It characterizes the current state of AI development and emphasizes the shift towards more dynamic and adaptable AI systems. Third Wave AI incorporates methods like deep learning, dynamical systems, neural networks, and generative models in addition to more conventional rule-based or statistical AI approaches. It aims to create AI systems that can understand, learn, and adapt to complex and dynamic environments.
Check out our guide on what to look for in an AI solution here.
Strengthening Security Defenses with Generative AI
Generative AI tools have the potential to enhance various aspects of cybersecurity, from data augmentation and malware detection to anomaly detection and security testing. By harnessing the power of Generative AI, organizations can strengthen their defenses, improve threat detection capabilities, and enhance their overall cybersecurity posture.
As the threat landscape continues to evolve, AI-enabled Cybersecurity solutions will become increasingly critical to maintaining strong defenses against security threats. Just watch out for those cybersecurity vendors selling snake oil.And when you’re ready, reach out to get a demo of a real AI-driven threat detection solution.
Other MixMode Articles You Might Like
AI Offers Potential to Enhance The U.S. Department of Homeland Security
Evolving Role of the CISO: From IT Security to Business Resilience